Introduction
Bitcoin mining in 2024 is witnessing unprecedented changes and challenges. The hashrate, a key metric in mining, has seen a significant increase, pushing past 600 EH/s on the 7-day average. This rise, coupled with a surge in transaction fees, has driven the hashprice to new heights, impacting mining profitability.
As Bitcoin rallies to $70,000 and faces frequent difficulty adjustments, miners must adapt to a volatile environment. Optimizing mining efficiency and production is crucial to staying competitive. This article delves into understanding hashrate and hashprice, the volatility in the mining market, and the strategic use of financial tools like hashrate forwards and futures to enhance mining operations.
Understanding Hashrate and Hashprice
Definition and significance of hashrate
In the realm of Bitcoin mining, hashrate refers to the total computational power used to mine and process transactions on the Bitcoin network. It is measured in hashes per second (H/s). The higher the hashrate, the more secure the network becomes, as it signifies a greater number of miners participating in the process. This increased participation makes it more difficult for any single entity to control the network or execute fraudulent activities.
Recent trends and statistics
In recent months, Bitcoin’s hashrate has seen a significant uptick, consistently staying above the 600 EH/s mark on a 7-day average. This trend highlights the growing interest and investment in Bitcoin mining, driven by the rising price of Bitcoin and the potential for lucrative returns. The increase in hashrate is also indicative of advancements in mining technology and the deployment of more efficient mining rigs, which can perform a higher number of hashes per second.
Impact of hashrate on mining operations
A higher hashrate generally means that more miners are competing to solve the complex mathematical puzzles required to add new blocks to the blockchain. This increased competition can lead to higher difficulty levels, as the Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty approximately every two weeks to ensure a steady rate of block creation.
For individual miners, a higher hashrate can mean reduced chances of successfully mining a block unless they have access to top-tier mining hardware and efficient operations. Therefore, staying competitive in a high-hashrate environment often requires substantial investment in advanced mining equipment and access to cheap electricity.
Explanation of hashprice
Hashprice is another crucial metric in Bitcoin mining, representing the revenue miners earn per unit of hashrate, typically expressed as dollars per terahash per day ($/TH/day). Hashprice fluctuates based on several factors, including Bitcoin’s market price, transaction fees, and the network difficulty.
1. Factors affecting hashprice
Several factors influence hashprice, making it a dynamic and often volatile metric:
- Bitcoin’s Market Price:A higher Bitcoin price increases the potential revenue from mining rewards, thereby boosting hashprice.
- Transaction Fees:Transaction fees are paid by users to have their transactions included in the next block. During periods of high network activity, transaction fees can surge, significantly increasing miners’
- Network Difficulty:As the difficulty of mining adjusts to the total hashrate, higher difficulty levels can reduce the chances of successfully mining a block, thus impacting hashprice.
2. Recent surge due to transaction fees
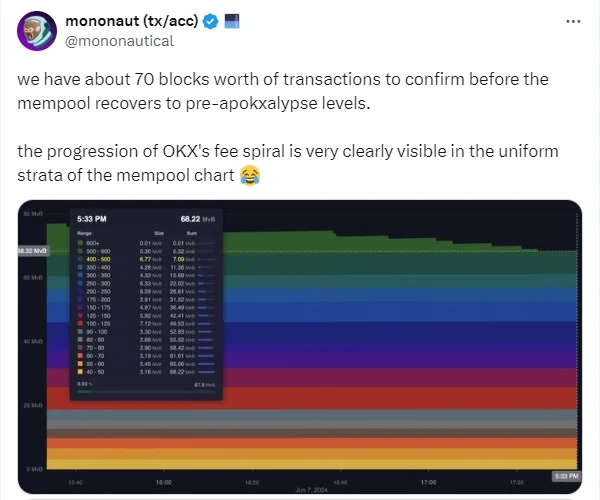
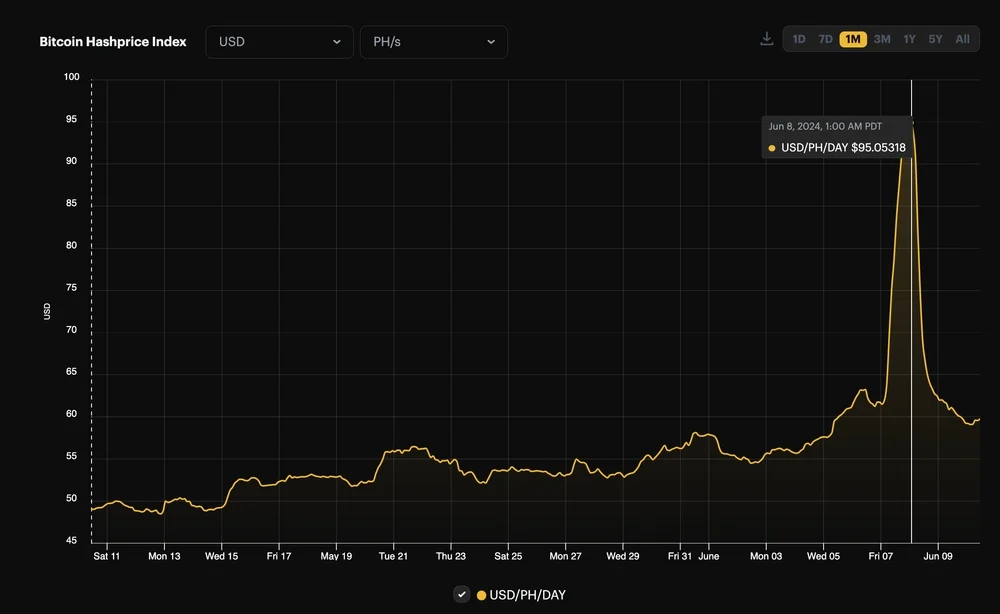
Recently, Bitcoin’s hashprice surged to $95/PH/day, primarily driven by an unexpected spike in transaction fees. This surge marked the highest point for hashprice since April 2024. The increase was largely attributed to OKX, a major exchange, which experienced issues with its UTXO (unspent transaction output) consolidation process. The exchange’s flawed transaction fee estimation algorithm led to a significant increase in transaction fees, driving up the hashprice. This incident underscores the sensitivity of hashprice to transaction fee dynamics and the importance of efficient transaction management by large network participants.
Volatility in the Bitcoin Mining Market
Causes of recent volatility
The Bitcoin mining market is no stranger to volatility. Recent fluctuations have been driven by several key factors that miners must understand to navigate this dynamic landscape effectively.
1. High transaction fees
One of the primary contributors to recent volatility has been the significant increase in transaction fees. In the past year, the Bitcoin network has seen several spikes in transaction fees, often linked to activities such as the trading of inscriptions, ordinals, and more recently, Runes. These activities inflate the size and frequency of transactions, leading to higher fees.
However, a notable spike in June 2024 was caused by OKX, a major cryptocurrency exchange, which experienced a glitch in its UTXO consolidation process. This bug led to OKX overbidding against its transactions, creating a feedback loop that significantly drove up transaction fees. Such sudden and substantial increases in transaction fees can cause hashprice to surge, affecting miners’ revenues and operational decisions.
2. Bitcoin rally and difficulty adjustments
Another major factor contributing to the market’s volatility is the ongoing rally in Bitcoin’s price. As Bitcoin’s value surged to $70,000, the attractiveness of mining increased, prompting more miners to join the network. This influx of miners boosts the overall hashrate, leading to subsequent increases in network difficulty. Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism, which recalibrates approximately every two weeks, ensures that blocks are added to the blockchain at a consistent rate.
However, during periods of rapid hashrate growth, difficulty adjustments can occur more frequently and with greater magnitude, impacting miners’ ability to predict and manage their operations efficiently. For instance, while there were five negative difficulty adjustments in the past year, the overall trend points towards increasing difficulty, which can squeeze profit margins for miners operating on the edge of profitability.
Effects of volatility on mining profitability
The inherent volatility in the Bitcoin mining market has significant implications for miners, particularly regarding profitability and operational stability.
1. Impact on revenue
Volatility in transaction fees and hashprice directly affects miners’ revenue streams. While higher transaction fees can boost short-term earnings, the unpredictability of these spikes can make it challenging to forecast long-term revenues accurately. Miners relying on steady cash flow may find it difficult to manage operational costs and plan for future investments when facing such uncertainty.
2. Operational challenges
Frequent and unpredictable difficulty adjustments pose additional challenges. As difficulty increases, miners must expend more computational power to maintain their share of block rewards. This often necessitates investments in more advanced and efficient mining hardware, which can be costly. Miners who fail to upgrade their equipment risk falling behind, as older, less efficient rigs become unprofitable in a high-difficulty environment.
3. Strategic adaptations
To cope with this volatility, miners need to adopt flexible and strategic approaches. This might include diversifying mining operations across multiple locations to mitigate risks associated with local power costs and regulatory changes. Additionally, leveraging financial instruments such as hashrate forwards and futures can provide miners with more predictable revenue streams and help manage the financial risks associated with operational volatility.
Strategic Use of Hashrate Forwards and Futures
Introduction to hashrate forwards and futures
In the volatile landscape of Bitcoin mining, financial instruments such as hashrate forwards and futures have become valuable tools for miners seeking to stabilize their operations and ensure consistent production levels. These instruments allow miners to hedge against fluctuations in hashprice and secure more predictable cash flows.
1. Definition and purpose
Hashrate forwards and futures are financial contracts that allow miners to buy or sell the right to a specific amount of hashrate at a predetermined price for a future date. The primary purpose of these instruments is to provide miners with a way to lock in prices and manage their exposure to the inherent volatility of the Bitcoin mining market. By securing a fixed price for hashrate, miners can better predict their revenue and plan their operations accordingly.
2. Benefits for Bitcoin miners
The use of hashrate forwards and futures offers several benefits to Bitcoin miners:
- Risk Management:These contracts help miners mitigate the risks associated with fluctuating hashprice and network difficulty.
- Capital Efficiency:Miners can secure capital through these contracts, enabling them to invest in new equipment and expand operations without immediate outlays.
- Operational Stability:By locking in hashrate prices, miners can ensure more stable and predictable revenue streams, which aids in long-term planning and operational management.
Strategies for using forwards and futures
To fully leverage the benefits of hashrate forwards and futures, miners can adopt several strategic approaches. These strategies not only help manage risk but also enhance overall mining efficiency and production capacity.
1. Buying hashrate forwards or futures
One effective strategy for miners is to purchase hashrate forwards or futures contracts. This approach allows miners to secure a set amount of hashrate at a fixed price, which can be particularly beneficial during periods of equipment downtime or market uncertainty.
- Mitigating downtime
Mining operations can experience unexpected downtime due to various factors such as equipment failure, power outages, or delays in the delivery of new ASICs. By purchasing hashrate forwards or futures, miners can compensate for these downtimes and maintain their production targets. For instance, if a miner’s equipment is offline due to maintenance, they can still fulfill their hashrate commitments and continue earning revenue through these financial instruments.
- Example scenario
Consider a miner who has planned to generate 3,500 PH/s from their infrastructure but faces energy issues that reduce their effective hashrate to 2,500 PH/s. To cover this shortfall, the miner can purchase 1,500 PH/s through a hashrate forward contract from Luxor. This allows them to meet their production target of 84 BTC per month despite the downtime, ensuring operational continuity and revenue stability.
2. Selling hashrate forwards for upfront capital
Another strategic approach is selling hashrate forwards to secure upfront capital. This method enables miners to finance the purchase of new ASICs or other operational expenses without dipping into their retained earnings or diluting shareholder value.
- Financing ASIC purchases
By selling future hashrate production, miners receive immediate payment, which can be used to purchase advanced mining hardware. This upfront capital allows them to expand their operations and improve efficiency without the financial strain of immediate expenditures.
- Impact on production capacity
Securing upfront capital through the sale of hashrate forwards can significantly enhance a miner’s production capacity. With access to the latest ASIC technology, miners can increase their hashrate and competitiveness in the market. This strategy also provides a buffer against future volatility, as the upfront funds can be used to optimize operations and withstand periods of lower hashprice or higher network difficulty.
Market Trends and Predictions
Current trends in ASIC market
The Bitcoin mining hardware market, particularly the ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) segment, is experiencing significant shifts. These trends are crucial for miners to understand as they influence both the cost and efficiency of mining operations.
1. Price trends for next-generation rigs
In recent months, prices for next-generation ASIC rigs have been on the rise. Models such as the S21 series are highly sought after due to their superior efficiency and higher hash rates. This increase in demand has driven up prices, making it more expensive for miners to upgrade their hardware. The higher initial costs are often justified by the long-term benefits of reduced electricity consumption and increased computational power, which enhance overall profitability. However, the rising prices can be a barrier for smaller or less capitalized miners, making it essential to plan hardware purchases strategically.
2. Decreasing value of older models
Conversely, the value of older ASIC models has been steadily decreasing. As new, more efficient models are introduced, older rigs become less competitive and more costly to operate relative to their output. This depreciation presents a challenge for miners still using older hardware, as they must either upgrade to maintain profitability or face diminishing returns. On the flip side, for new entrants or smaller operations, acquiring these older models at lower prices can be a cost-effective way to enter the mining market, albeit with lower efficiency.
Future predictions for Bitcoin mining
Looking ahead, several factors are expected to shape the Bitcoin mining landscape, influencing both the hashrate and hashprice.
1. Potential for increased difficulty adjustments
As more miners enter the network and technological advancements continue, the Bitcoin network’s difficulty level is likely to increase. Difficulty adjustments occur approximately every two weeks to maintain a consistent block creation rate, regardless of the total hashrate. With the growing adoption of next-generation ASICs, the hashrate is expected to rise, prompting more frequent and significant difficulty adjustments. These adjustments will necessitate ongoing investment in high-efficiency mining equipment to remain competitive. Miners who fail to keep pace with these changes may find their operations becoming increasingly unprofitable.
2. Long-term outlook for hashrate and hashprice
The long-term outlook for hashrate and hashprice involves both opportunities and challenges:
- Hashrate:The global hashrate is projected to continue its upward trend, driven by increased participation from institutional miners and advancements in mining technology. This growth in hashrate will enhance network security but also escalate the competition among miners.
- Hashprice:Hashprice is expected to remain volatile, influenced by factors such as Bitcoin’s market price, transaction fee fluctuations, and network difficulty. While periods of high transaction fees can temporarily boost hashprice, long-term stability will depend on broader market conditions and regulatory developments.
Strategically, miners must stay abreast of these trends and predictions to adapt their operations accordingly. Investing in cutting-edge hardware, optimizing energy usage, and leveraging financial instruments like hashrate forwards and futures will be critical for sustaining profitability in a rapidly evolving market.
Practical Tips for Bitcoin Miners
Navigating the complexities of Bitcoin mining requires a blend of strategic planning, constant monitoring, and adaptability. Here are some practical tips to help miners optimize their operations and stay competitive in the ever-evolving mining landscape.
A. Monitoring and adapting to market changes
1. Importance of staying informed
Staying informed about market trends and industry developments is crucial for Bitcoin miners. The cryptocurrency market is highly dynamic, with frequent changes in hashprice, network difficulty, and transaction fees. Miners need to keep abreast of these changes to make timely decisions that can impact their profitability. Subscribing to industry newsletters, participating in mining forums, and using real-time monitoring tools can help miners stay updated on the latest trends and data.
2. Tools and resources for real-time updates
Several tools and resources can provide real-time updates and insights for miners:
- Mining Pools and Platforms:Platforms like Hashrate Index and major mining pools offer real-time data on hashrate, difficulty, and profitability metrics.
- Market Analytics Tools:Tools such as Coin Metrics and Glassnode provide in-depth analysis and visualizations of market trends and blockchain data.
- News Aggregators:Websites and apps that aggregate cryptocurrency news, such as CoinDesk and CryptoSlate, can help miners stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and market movements.
B. Implementing strategic financial instruments
1. Utilizing hashrate forwards and futures
Financial instruments such as hashrate forwards and futures offer miners a way to hedge against market volatility and secure more predictable revenue streams. Here’s how miners can utilize these tools effectively:
- Hedging Against Volatility:By locking in a fixed price for hashrate through forward or futures contracts, miners can protect themselves from unfavorable market fluctuations. This is particularly useful during periods of high volatility when hashprice can vary significantly.
- Planning for Equipment Upgrades:Selling future hashrate through these contracts can provide miners with upfront capital needed for purchasing new equipment or expanding their operations. This ensures that they can remain competitive without straining their finances.
2. Leveraging firmware for efficiency
While this section was initially intended to include firmware strategies, focusing solely on financial instruments provides a clear and targeted approach. By concentrating on financial tools, miners can better manage their economic risks and ensure long-term operational stability.
Utilizing hashrate forwards and futures effectively involves:
- Risk Assessment:Miners should assess their risk tolerance and operational needs before engaging in these contracts. Understanding the terms and potential outcomes of each contract is crucial.
- Collaborating with Experts:Engaging with financial advisors or experts in cryptocurrency derivatives can help miners navigate the complexities of these instruments and maximize their benefits.
C. Diversifying Mining Strategies
1. Geographic Diversification
Operating mining rigs in different geographic locations can mitigate risks associated with regional power outages, regulatory changes, and environmental factors. Diversifying locations also allows miners to take advantage of varying electricity costs and renewable energy sources.
2. Energy Efficiency
Investing in energy-efficient mining hardware and exploring renewable energy options can significantly reduce operational costs. Additionally, energy-efficient practices can help miners maintain profitability even during periods of low hashprice.
3. Continuous Optimization
Regularly reviewing and optimizing mining operations is essential for maintaining competitiveness. This includes keeping software up to date, ensuring optimal cooling systems, and continually assessing the performance of mining rigs.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin mining landscape in 2024 presents both challenges and opportunities for miners. Key developments such as the rise in hashrate and the surge in transaction fees have significantly impacted the market. Understanding the interplay between hashrate and hashprice is essential for optimizing mining operations and maintaining profitability. Market volatility, driven by factors such as high transaction fees and fluctuating Bitcoin prices, necessitates strategic adaptations by miners.
Leveraging financial instruments like hashrate forwards and futures provides a valuable means of managing risk and securing predictable revenue streams. These tools can help miners mitigate the effects of downtime and secure upfront capital for equipment purchases. Current trends in the ASIC market, including rising prices for next-generation rigs and the declining value of older models, underscore the importance of strategic planning and timely upgrades.
Practical tips for miners include staying informed about market changes, utilizing real-time monitoring tools, and adopting diversified mining strategies. Geographic diversification, energy efficiency, and continuous operational optimization are critical for sustaining profitability in a competitive environment.
Maximizing Bitcoin mining efficiency and production in 2024 requires a proactive and informed approach. Miners must stay ahead of market trends, leverage strategic financial tools, and continually optimize their operations. By doing so, they can navigate the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market and capitalize on opportunities for growth.
The dynamic nature of Bitcoin mining calls for adaptability and strategic foresight. Miners who invest in advanced hardware, adopt innovative financial strategies, and remain agile in their operations will be well-positioned to thrive in 2024 and beyond. As the industry continues to evolve, staying informed and making data-driven decisions will be the keys to success.